What is the difference between solar cells and photovoltaic modules?
As the world increasingly turns to renewable energy, solar energy has become a leader in reducing carbon emissions and combating climate change. At the heart of this technology are solar cells and photovoltaic (PV) modules, which play a vital role in harnessing the sun’s energy. However, many people often confuse the two terms. In this article, we’ll explore the differences between solar cells and PV modules while examining the broader context of solar PV systems and their market potential.

Understanding Solar Cells
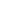
Solar cells, also known as photovoltaic cells, are a fundamental building block of solar technology. These devices convert sunlight directly into electricity through the photovoltaic effect. When sunlight strikes the surface of a solar cell, it excites electrons, creating an electric current. Solar cells are typically made from semiconductor materials, such as silicon, which are known for their efficiency in converting sunlight into electricity.
The efficiency of a solar cell is a key factor in determining how much electricity can be generated from a given amount of sunlight. Technological advances have led to the development of various types of solar cells, including single crystal, multi-crystalline, and thin-film cells, each with their own advantages and disadvantages in terms of efficiency, cost, and applications.
What are photovoltaic panels?
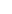
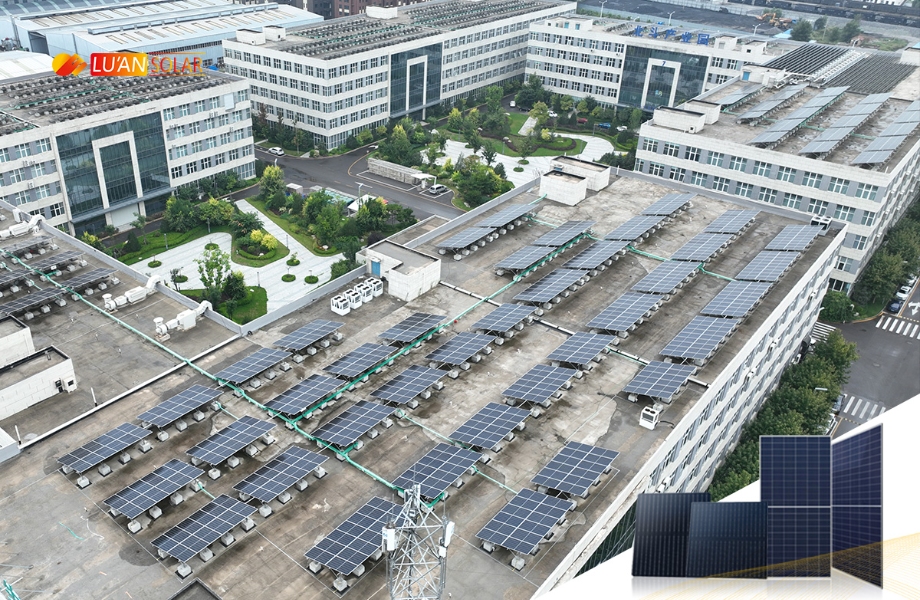
Photovoltaic modules, commonly known as solar panels, are multiple solar cells connected together to form a larger unit. Photovoltaic modules are designed to capture sunlight and convert it into electricity that can be used for residential, commercial and industrial purposes. The main purpose of a photovoltaic module is to increase the surface area available for absorbing sunlight, thereby increasing the total energy output of a solar photovoltaic system.
Photovoltaic panels are typically encased in protective materials to protect them from environmental conditions such as rain, wind and hail. They are also equipped with electrical components that help convert the direct current (DC) generated by the solar cells into alternating current (AC), the standard form of electricity used in homes and businesses.
The main differences between solar cells and photovoltaic modules
Composition: The most fundamental difference between solar cells and photovoltaic modules is their composition. Solar cells are individual units that use sunlight to generate electricity, while photovoltaic modules are a collection of these cells designed to work together to produce higher power output.
Functionality: The main function of solar cells is to convert sunlight into electrical energy. Photovoltaic modules are designed to optimize this process by maximizing the surface area that absorbs sunlight and providing a protective structure for the solar cells.
Output: A single solar cell typically produces a small amount of electricity, usually around 0.5 to 0.6 volts. In contrast, a photovoltaic module can contain 36 to 72 solar cells and can produce a lot of electricity, typically 250 to 400 watts or more, depending on the design and efficiency of the module.
Application: Solar cells are primarily used in R&D environments or small applications such as calculators and small electronic devices. PV modules, on the other hand, are used in large-scale solar PV systems for residential, commercial, and utility-scale energy production.
Solar Photovoltaic System
A solar photovoltaic system consists of multiple components, including solar cells (or photovoltaic modules), inverters, mounting systems, and sometimes battery storage systems. The inverter plays a vital role in converting the direct current generated by the solar cells into alternating current, which can be used in homes and businesses or fed back into the grid.
Mounting systems hold the PV panels in place, ensuring they are in the best position to capture sunlight throughout the day. In some cases, battery storage systems are integrated into solar PV systems to store excess energy generated during the day for use at night or when there is less sunlight.
Market Potential
The global solar photovoltaic (PV) market is experiencing rapid growth, driven by the growing demand for renewable energy and advancements in solar technology. According to recent estimates, the global solar PV market size is expected to be approximately $179.69 billion in 2024 and is expected to reach approximately $451.23 billion by 2030. This growth is driven by government incentives, falling costs of solar technology, and growing awareness of the environmental benefits of solar energy.
As more individuals and businesses invest in solar photovoltaic systems, demand for solar cells and photovoltaic modules will continue to rise. This trend highlights the importance of understanding the differences between these components and their role in the broader context of solar power generation.
In summary, while solar cells and PV panels are often used interchangeably, they play different roles in the solar energy sector. Solar cells are stand-alone units that convert sunlight into electricity, while PV panels are components of these cells designed to maximize energy output. As the solar PV market continues to expand, understanding these differences is essential for anyone looking to invest in or utilize solar energy solutions. With the potential for significant growth in solar energy in the coming years, the future of solar energy is bright, paving the way for a more sustainable, greener energy landscape.