Types of Solar Panels: Understanding Efficiency and Making the Right Choice
The fast-paced world of solar technology often makes efficiency rates range from 10 percent to more than 22 percent (and counting!). With the overwhelming variety of options available, homeowners can feel anxious comparing the varieties available.
The fact is, there is no one “best” solar panel—your neighbor’s solar panel may not meet your specs appropriately. Depending on your situation, different types of solar panels offer different efficiencies, looks, long-term durability, and costs.
We will review the primary differences between monocrystalline, polycrystalline, thin-film, and other new solar technologies.
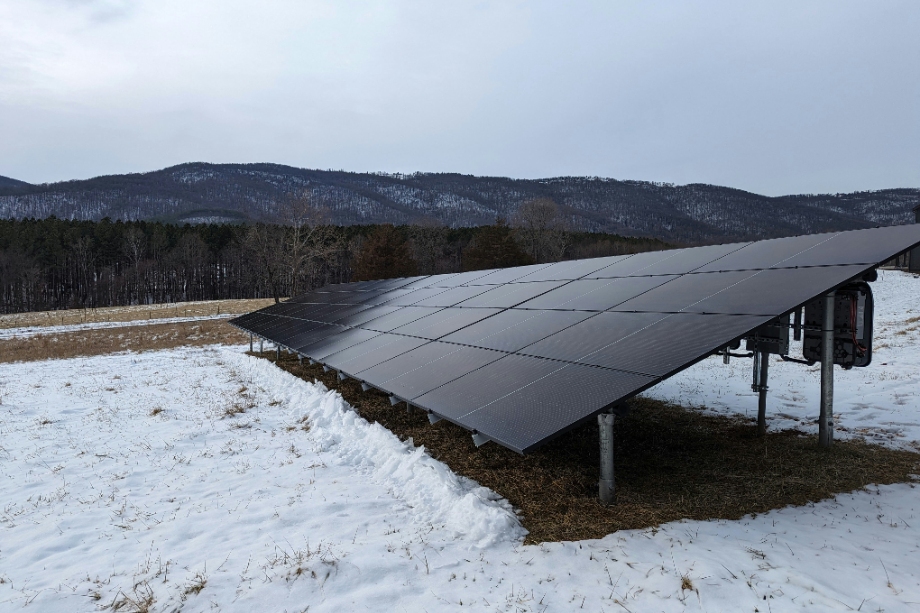

What is a Solar Panel Efficiency?
In general terms, a solar panel’s efficiency is how well the panel converts sunlight into usable electricity. A higher-efficiency means that more power will be produced from the same amount of sunlight. Solar panel efficiencies range from 10 percent for thin-film to over 22 percent for Monocrystalline panels, depending on which technology is used.
So why does efficiency matter?
● Higher-efficiency panels will take up less roof space, which is important for homeowners with limited roof space.
● More efficient panels will generally produce more electricity than lower-efficiency panels.
● Higher-efficiency panels tend to perform better in low-light situations, which is important for performance in effectively producing power in cloudy situations.
● Higher-efficiency panels can yield far more savings in the long run, and may justify their higher upfront costs.
Major Types of Solar Panels and Their Efficiencies
If you are looking at types of solar panels on the market today, knowing the efficiency ratings will help you assess which solar panels will suit your needs best. You may have a choice from several basic varieties.
Monocrystalline Solar Panels
Efficiency Range: 17-22%
Monocrystalline panels are made from a single-crystal silicon (a black solar panel). Monocrystalline solar panels consist of single crystal formations that provide better electron flow, and therefore better efficiency.
Key points:
-Made with pure silicon, uses waifers of it.
-Obsidian black color and the most consistent look
-Lasts longer (25+ years)
-Better efficiency in hot weather
-Higher cost per panel
Monocrystalline panel’s are best for small rooftop applications where maximising energy production per square foot is important. They also look beautiful, minimal, and are generally a better cosmetic option for visible installations.
Polycrystalline Solar Panels
Efficiency Range: 15-17%
Polycrystalline panels are made by melting a number of silicone shards together which naturally results in their blue and dimensional appearance. The energy required to make polycrystal is less for manufactures as well, leading to a lower price.
Key points:
-Pure silicone, several different crystals in each panel
-Blue tinted speckled look
-Slightly shorter lifespan compared to Monocrystalline
-Slightly cheaper than Monocrystalline
-Slightly less tolerant of heat
Polycrystalline panels are a decent midpoint between cost and efficiency and are better suited to larger applications where space is not as limited, allowing for less emphasis on the amount of energy production per square ft.
Thin-Film Solar panels
Efficiency Range: 10-13%
Thin film panels use a very thin layer of photovoltaic material on a substrate of glass, plastic or metal. While their efficiency refers to the actual conversion rate of the solar energy into usable energy per square foot, thin film panels do already offer a number of value propositions to their applications.
Key points:
-Flexible, light weight
-Uniform black visual
-More tolerant of high temperatures
-Offers lower efficiency as more space for mounting
-Lifespan: 15-20 years
Thin film’s added flexibly in design and unique applications give them potential for curved surfaces, portable applications and building integrate photovoltaics where traditional rigid panels could not.
PERC Solar Panels
Efficiency Range: 17-20%
PERC technology takes a traditional monocrystalline panel and changes it slightly with an additional reflective layer to collect more light energy usage from the sun.Type of solar panels which is comparable somewhat to traditional solar panels but offers a reflective layer
Key features:
● Minor deviation with the base mono crystalline panel
● Higher performance in low light
● More efficient than traditional mono panels
● More efficient in hotter environments
● Additional cost for this upgrade
Overall, PERC technology is an advancement in efficiency, it has shown continued enhancement with no major price increase and is beginning to penetrate more residential installations.
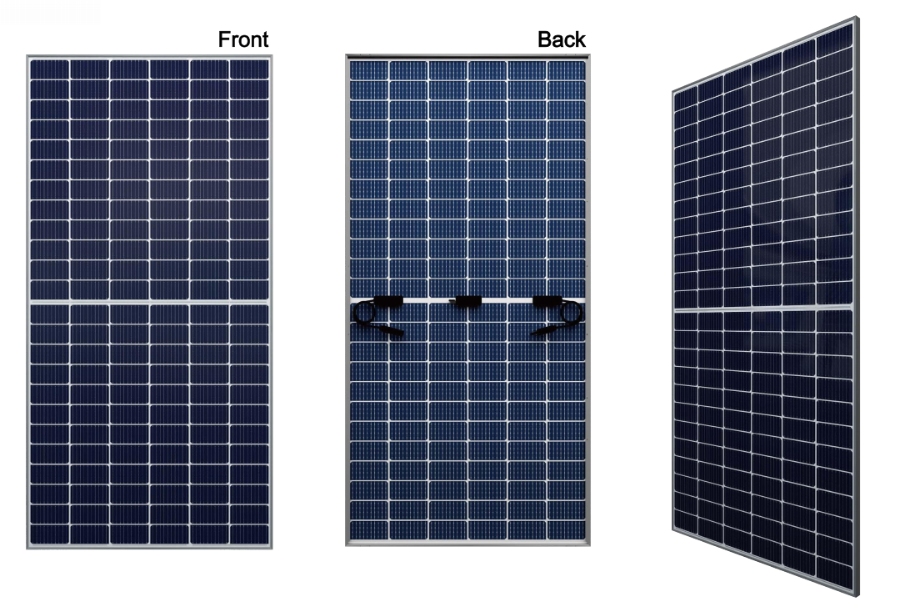
Bifacial Solar Panels
Efficiency Range: 15-22% (front) + as much as 30% from the rear;
Bifacial or dual solar panels receive energy production from both sides in that it can receive direct light from the front side but also receive reflected light from the rear side. The overall combination of power output is a much larger output than traditional one-sided (non-bifacial) panels.
Key features:
● Power generation on both sides
● Usually frameless glass
● Requires a reflective surface beneath the panel itself to gain additional light
● More complex installation
● Potential increased effective lifespan of the panels
It is typically best for these panels to have light colored roofs, a ground mount above a reflective ground, or a tracking system All these design-impact strategies would increase the potential of the dual sided advances.
HJT (Heterojunction Technology) Solar Panels
Efficiency Range: 19-24%
HJT panels have a blend between crystalline silicon and thin film technology to create a hybrid panel that achieves some impressive efficiency ratings. This technology is still relatively new but it’s already seen some traction in a higher level install market. Main characteristics:
● Lower Temperature Coefficients
● Higher Low Light Performance
● Higher performance in hotter climates
● Higher Price
● Longer Performance Warranty
For homeowners, the people who want to ensure they are purchasing high efficient solar panels for their home, HJT technology is one of the highest level of technology available on the market today in the residential market.
Which Type of Solar Panel Is Most Efficient?
In terms of the current market based on efficiency numbers, here is the current market.
1. IBC/N-type Cells (SunPower/Maxeon): 20-24%
2. HJT Panels: 19-24%
3. Monocrystalline: 17-22%
4. PERC: 17-20%
5. Polycrystalline: 15-17%
6. Thin Film: 10-13%
That being said, efficiency is only one of the factors to consider, the most efficient solar panel for your situation will depend on the following:
● Available space for installation: less installation space = higher efficiency panel preferred
● Climate: not all panels perform the same in heat and low light conditions
● Price: higher efficiency also equals higher price
● Aesthetics: depending on your home, the panels can all look different
● Installation location: e.g roof vs ground

Factors Beyond Efficiency to Consider
Efficiency does tend to dominate the conversation, however there are some other considerations in your selected solar panel:
Temperature Coefficient
The temperature coefficient measures how much a panels efficiency drops with increase in temperature. HJT and thin film technologies often improve temperature coefficient so their performance may be better in hot conditions, even though they are rated efficiency is lower.
Degradation Rate
All solar modules are going to degrade over time. Premium panels can degrade as low as 0.3% per annum while standard panels can degrade 0.5-0.7% per annum. After 25 years it could be a large amount of lost energy production!
Warranty
Most panels are sold with product warranties (10-25 years) and power production warranties (25-30 years). Normally, premium high efficiency panels generally have better warranties.
Space
If you are limited on roof space in your installation, higher efficiency panels will just be more expensive for you. If you are doing a ground mount installation with ample space, lower efficiency can mean a lot of value.
Making the Right Choice for Your Situation
When purchasing solar panels, match the technology and panel to your needs, whether it is efficiency, price or space.
1. Limited roof space = Monocrystalline or HJT or IBC for higher power density panels.
2. Price restrictions = Polycrystalline or standard PERC panels.
3. Hot climates = Lower temperature coefficients, e.g. HJT or thin film.
4. Snow = Bifacial panels can utilize light reflected off the snow.
5. Aesthetics = Black monocrystalline panels can look sleeker.
Conclusion
Monocrystalline and HJT Panels are currently the highest efficiency panels commercially available but which is best for you will depend on your situation. By now, you have a good understanding of the type of panels available and the intricacies involved with efficiency, as well as some options that meet your performance, budget and practical requirements.
It is also important to understand the solar technology space changes quickly; you see new products every year that improve efficiency. Again, be sure to reach out to educated solar professionals whom can take your preferences with energy requirements, installation location and budget into account and help you determine the best type of panel for your solar installation.